AVENCOM has been involved in several projects that have required the use of fiber optic sensors and optical signal processing since 2003.
Distributed fiber optic sensing has unique features that leave it far ahead of other sensing technologies in some particular fields. The ability to measure temperatures and strain at thousands of points along a single fiber is particularly interesting for the monitoring of elongated structures such as pipelines, flow lines, oil wells, and pipe racks.
In the Oil and Gas industry distributed acoustic/vibration sensors and distributed temperature sensors are used in the following applications:
- Pipeline Intruder Detection and Third Party Interference Detection;
- Downhole distributed flow measurement and monitoring in wells;
- Pipeline Leak Detection;
- Pig Tracking;
- Production area perimeter control;
- Hot spot detection in high-power cables.

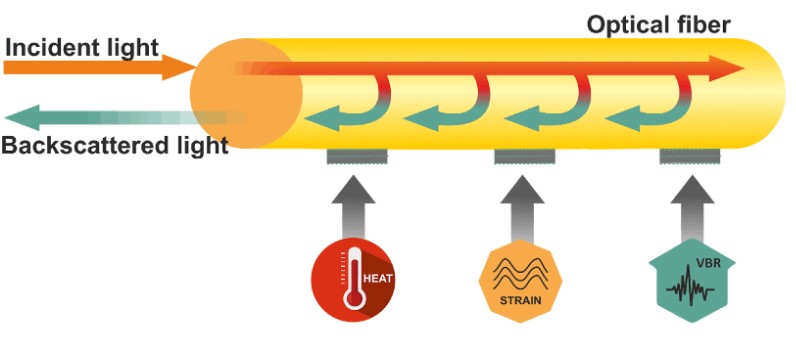
- Optical fiber-based distributed sensing is based on monitoring changes to the intrinsic properties of the light within the fiber when it is exposed to environmental changes.
- Distributed sensing system based on light scattering effects in standard telecommunication-grade optical fiber is powerful tool for analyzing spatially resolved profiles of physical quantities along fiber-optic cables.
- The method uses a technique called Coherent Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (C-OTDR)
Optical fiber as a monitoring tool
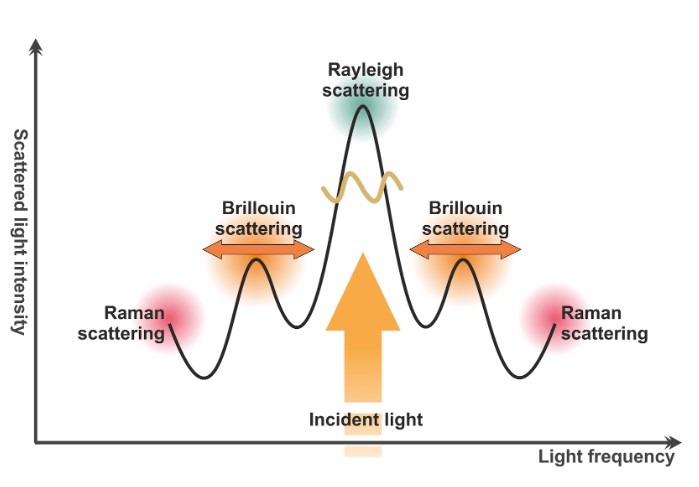
- Optical fibers exhibit three scattering processes that have been found to be extremely useful in measuring physical quantities: Brillouin, Raman, and Rayleigh scattering
- Each scattering process shows a characteristic spectrum with specific dependencies on the physical quantities to be analyzed
Light-scattering mechanisms
Optical measurands and physical parameters in scattering processes in optical fibers.
| Scattering process | Optical measurands | Physical parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Raman | Amplitude (anti-Stokes, Stokes) | Temperature |
| Brillouin | Frequency, amplitude | Temperature, strain |
| Rayleigh | Amplitude, phase | Dynamic strain and temperature |
- Brillouin and Raman scattering are inelastic scattering processes involving energy transfer to or from thermal vibrations (optical and acoustic phonons, molecular vibrations)
- Rayleigh scattering is elastic scattering caused by static inhomogeneities of the refractive index.
- Measuring the amplitude of the Rayleigh signal is sufficient for sensitive detection of events with broad acoustic spectrum like walking, driving and digging. That is why it is used in Distributed Acoustic Sensing
Principle of operation
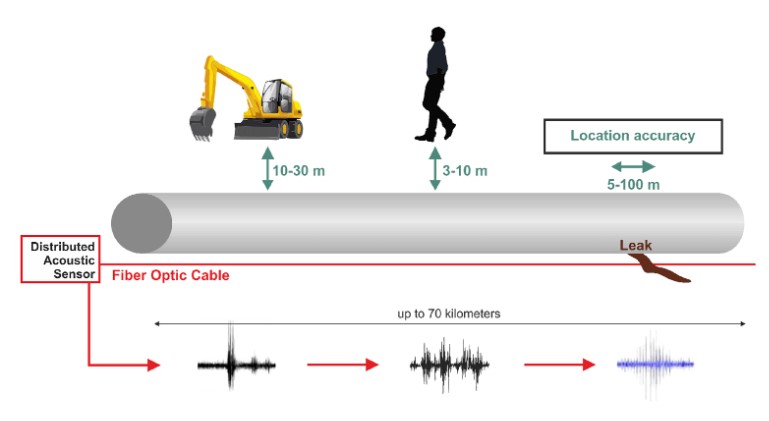
- Optical sensor unit constantly launches a high frequency light pulse through the fiber and analyses the backscattered spectrum.
- Any activity up to a certain distance from the fiber for instance a pipe leak or third party interference into a pipeline operations, produces acoustic energy.
- This causes a phase shift in the backscattered spectrum that is analyzed.
- The location of an event results from measuring the time that has lapsed between launching of the pulse and receipt of the backscattered light.
Event identification
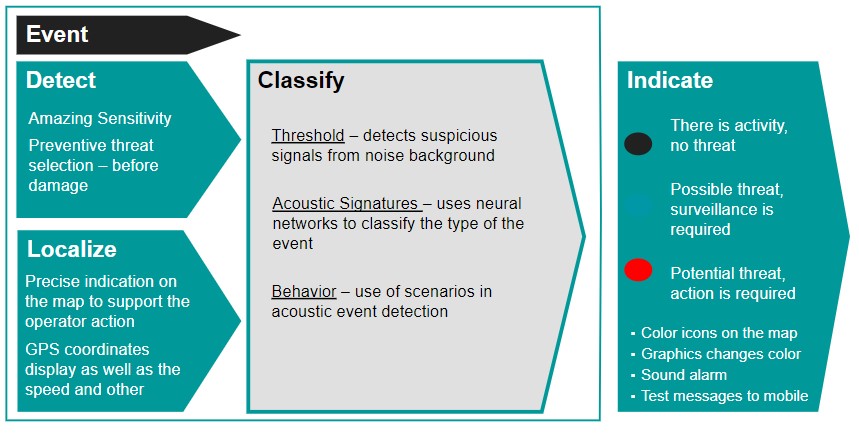
- DAS does not only detect and locate an event but can even identify its nature.
- Acoustic energy can be generated by a wide range of events, from a leak in a pipe line to footsteps, vehicles, cutting of a cable, etc.
- Each of these events has a unique acoustic footprint that is recognized.
DAS system Applications

Pipelines monitoring
- DAS system provides a timely warning for third party activities such as digging and ground works inside of operation zone.
- It is the solution for leak detection of existing underground pipelines.
- DAS system is now capable of taking in the majority of leak related signals that can be delivered by a single fibre optic cable.
Perimeter security
- System identifies a large variety of activities such as footsteps, type of vehicle, climbing or cutting a fence.
- The underground fiber cable is invisible and undetectable, is immune to electromagnetic induction.
- DAS monitors every meter of the perimeter 24 hours per day on a real-time basis.

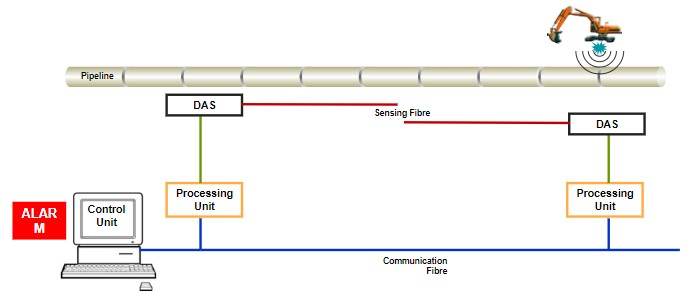
DAS system deployment
The focus for DAS is the Oil & Gas industry where pipelines are exposed to significant threats (intentional and unintentional).
- Today it is estimated that over 20,000 km of pipeline worldwide are currently being monitored using DAS systems.
- Operation range up to 70 km in one direction (140 km in extended configuration).
- Three physical connections at the installation site: telecom fiber cable (does not need to be close to the pipe), power supply (230VAC or 48VDC), CAT5 Ethernet.